Learner-centered Instruction
Definition
Learner-centered instruction empowers learners to participate actively in the learning process. Unlike more traditional teacher-centered approaches which focus on the instructor, this model places the learner at the center of the learning process. The role of the instructor goes beyond transmitting knowledge, as they take on the responsibility of facilitating active learning experiences for the learners. At the same time, learners take on a more proactive role, influencing course content and activities and actively reflecting on their learning.
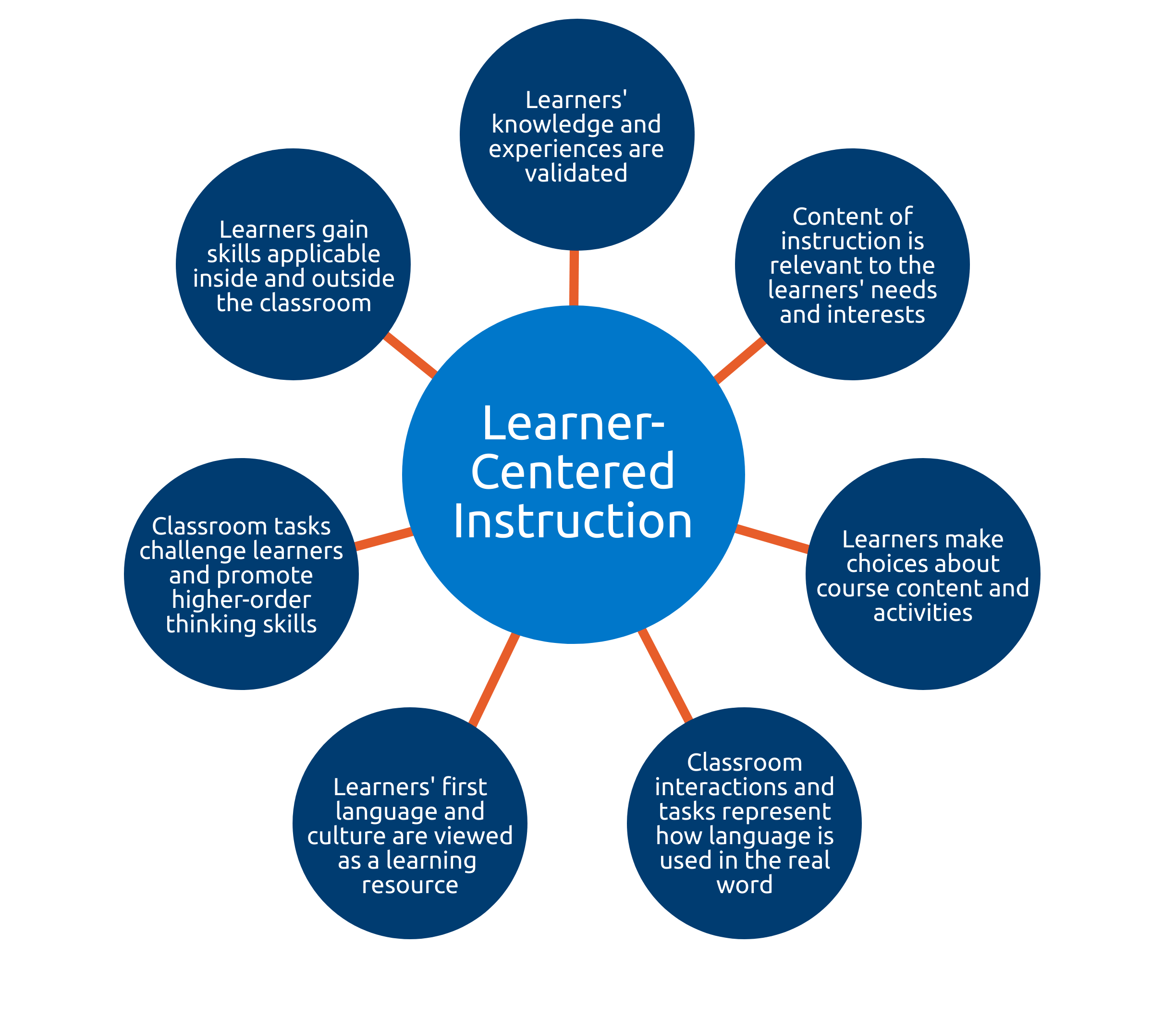
Explanation
The focus shift from teacher-centered to learner-centered instruction allows us to empower learners to take control of their own learning processes. This approach moves away from covering content to employing content in order to help learners develop skills that will be applicable to real-world situations. Through authentic assessments and feedback, learners have the opportunity to reflect on what they are learning and how they are learning it.
The table below provides a comparison between teacher-centered and learner-centered instructional models.
Teacher-centered Instructional Model |
Learner-centered Instructional Model |
|
Places the instructor at the center of the learning process |
Places the learner at the center of the learning process |
|
Instructor imparts knowledge, not involving learners in the learning process |
Instructor serves as a facilitator, involving learners in the learning process |
|
Instructor chooses topics and activities; learners participate passively |
Learners influence topics and activities and participate actively |
|
Assessments are one-dimensional and focus on grading |
Assessments are multidimensional and provide ongoing feedback |
|
Prioritizes memorization and correctness |
Prioritizes higher-level thinking |
|
Academic culture is competitive and individualistic |
Academic culture is collaborative and supportive |
Application
Weimer (2013) describes 5 key changes to practice:
- Balance of power: challenge the traditional power structure and the role of authority in the classroom.
- Function of content: focus on higher-order thinking rather than memorization, allowing learners to actively explore and reflect on their learning.
- Role of the instructor: serve as a facilitator that promotes learning rather than a content expert or authoritarian classroom manager.
- Responsibility of learning: promote independent, active and autonomous learning, as learners become more responsible for their own learning.
- Evaluation purposes and processes: utilize assessments as tools to promote learning and not tools to generate grades. Incorporate authentic assessments with meaningful, ongoing feedback.
References
Parrish, B. (2019). Teaching Adult English Language Learners: A Practical Introduction Paperback (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice (2nd ed.). Jossey-Bass.