Assessments
Definition
Assessment strategies allow the teacher and learner to determine what learning is taking place and has taken place. Assessments can occur before learning, as diagnostic assessments, to determine what the learner already knows; during learning through formative assessments; and at the end of learning as a summative assessments or evaluations.
Explanation
Diagnostic Assessment |
Formative Assessment |
Summative Assessment |
|
What: assessment for learning; what learners already know When: Before learning Why: to determine the learner’s level of understanding prior to the lesson; used to adjust instruction to meet learner needs Examples:
|
What: assessment for and as learning; monitors learner progress throughout learning When: During learning Why: to provide feedback, identify gaps and adjust instruction to maximize student achievement Example:
|
What: assessment of learning; evaluation of learning at the end of a unit or course When: After learning Why: to evaluate student learning against learning outcomes Examples:
|
Application
Consider what you are assessing at each level of assessment (diagnostic, formative, and summative) including the knowledge and skills required for learners to achieve course outcomes.
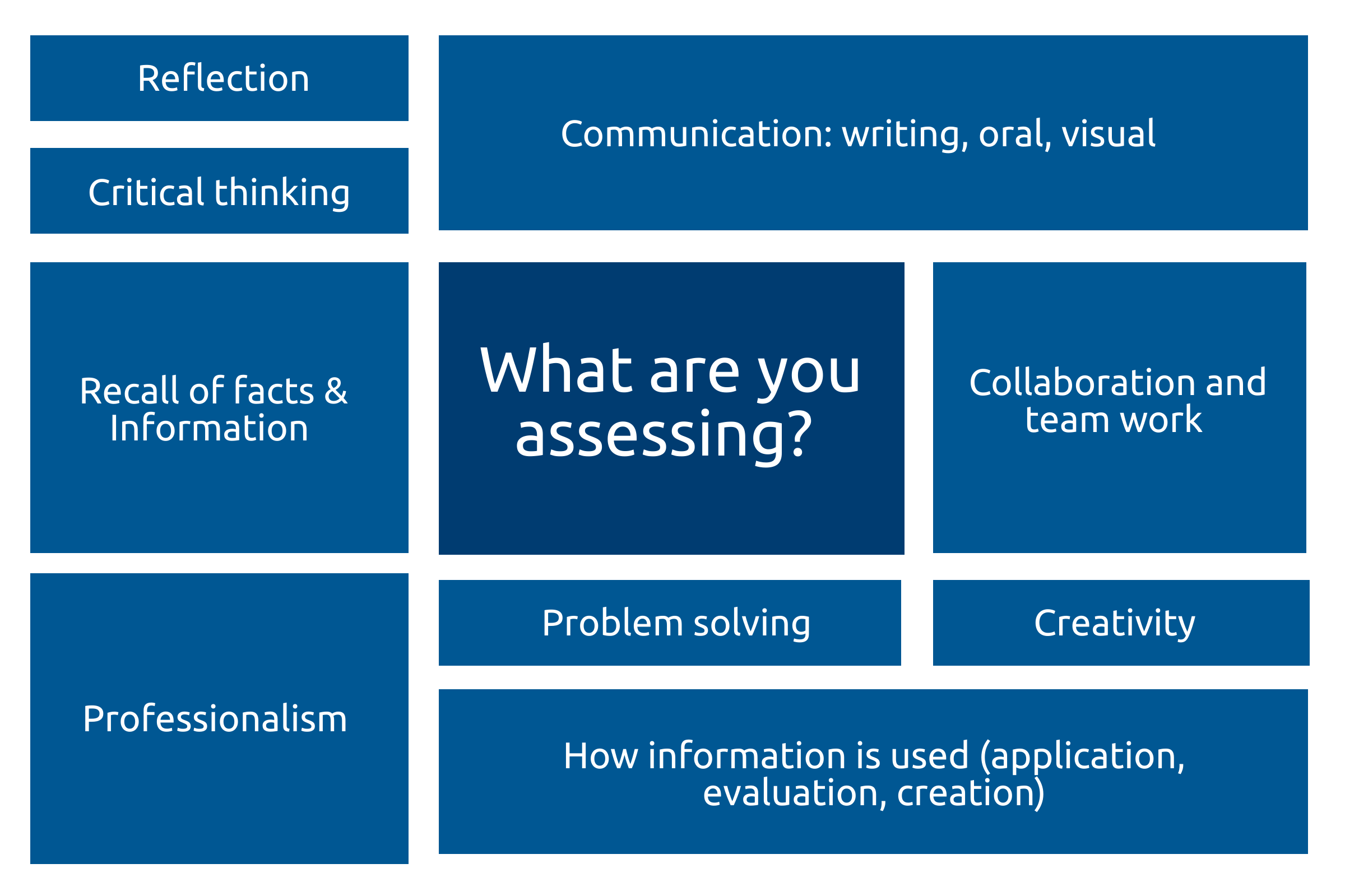
Knowledge and skills can be assessed in the following ways:
Diagnostic and Formative Assessments
- Minute papers
- Exit tickets
- Practice quizzes
- Learning logs, reflective journals, or course blogs
- Self and peer assessments
- Live question poll/survey response
Summative Assessment/Evaluation
- Oral exams or final presentations
- Digital portfolios
- Research posters
- Research papers
- Wikis
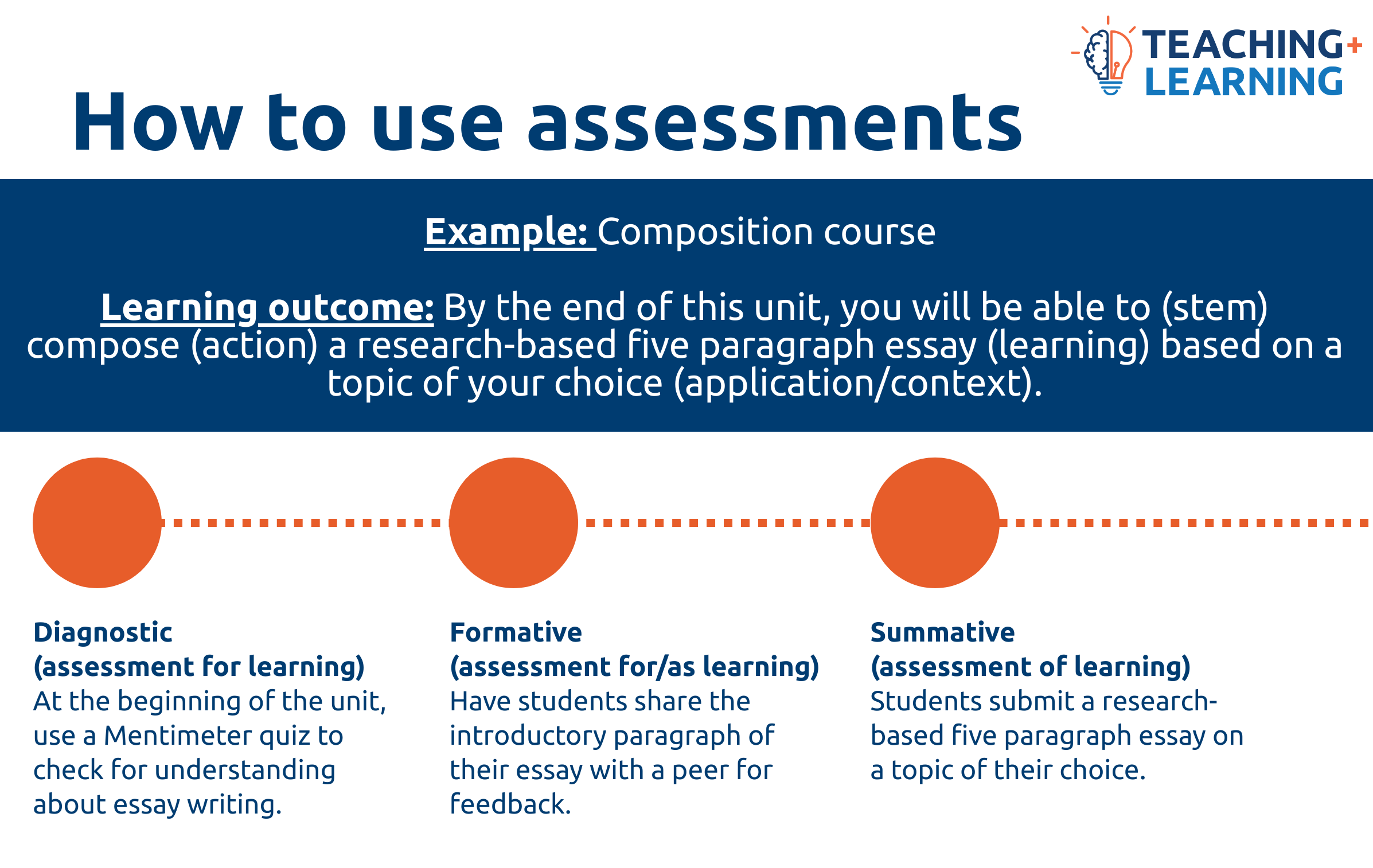
Example
Resources
Assessment Strategies. Queen’s University
Learner-Centred Assessment. University of Waterloo
